webdancer's Blog
matlab编程3—添加工具箱
在matlab程序设计中,如果我们要引入别人的写好的工具箱,怎么做呢?
首先,介绍一下matlab中的两个概念:current directory 和 search directory。matlab中的文件操作将这两个文件夹作为引用点,所以我们的文件必须在这两个之一。
1.current directory
current directory在matlab的GUI的matlab toolbars中默认显示,我们很容易更改current directory.如下图:
2.search directory
安装工具箱,就是将工具箱路径,添加到search directory中。
有两种方式:
- 命令行。addpath(genpath('/path/to/targettoolbox'))
- 通过GUI界面。选择File-->setpath添加。
注意:matlab中,搜索目录中的函数在统一命名空间,这样如果函数重名,是一个比较让人不好办的问题。如果自己写的函数,不要与matlab内置函数重名;如果第三方toolboxs有重名现象,只好改名了。
matlab编程2
matlab里面记录代码的文件成为M-files。可以分为两种类型:script和function。
1.script。不接受输入,也不返回输出。它对workspace的数据进行操作。和python等的脚本文件是一样的,把在控制台的命令给保存起来。
2.function。接受输入参数,返回输出。这类文件的一个注意的地方就是文件名和函数名必须相同.
例子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | function r = rank(A,tol)%RANK Matrix rank.% RANK(A) provides an estimate of the number of linearly% independent rows or columns of a matrix A.% RANK(A,tol) is the number of singular values of A% that are larger than tol.% RANK(A) uses the default tol = max(size(A)) * eps(norm(A)).%% Class support for input A:% float: double, single% Copyright 1984-2007 The MathWorks, Inc.% $Revision: 5.11.4.5 $ $Date: 2007/08/03 21:26:23 $s = svd(A);if nargin==1 tol = max(size(A)) * eps(max(s));endr = sum(s > tol); |
从这个例子中,看出:
1.从第一行看出,文件名与函数名一致。
2.%的行为注释,用help rank可以查看(当然,help方法删掉了一些没用的,比如最后两行)。
3.下面为函数体,是函数的实现。参数的参数数目可以用方法nargin和nargout获得。(n/arg/in)
function可以分为以下几种类型:
1.匿名函数。
不用创建专门的m文件,可在命令行,m文件内部创建。语法如下
1 | f=@(arglist) expression |
例子:
1 | >> sqrt=@(x) x.^(1/2); |
2.主函数和子函数。
函数类型的M文件需要一个主函数,放在第一位;后面可以跟若干个子函数(当然可以不跟)。
3.私有函数。
只对一些函数可见,放在名称为:private的目录下面。
4.嵌套函数。
在函数体内,定义新的函数。
提示:
构造字符串参数
用[]可以连接字符串,很容易来构造所需要的参数。
例子:
1 2 3 4 | for i=1:10, s=['index' int2str(i) '.dat']; load(s);end |
特殊的函数:
eval:可以执行matlab命令。
例子:
1 2 | >> cmd='1+1';>> eval(cmd) |
函数句柄:
使用@符号,可以获得matlab函数的句柄。这通常在把matlab函数作为参数的时候非常有用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | function [f,g] = myfun(x)f = 3*x(1)^2 + 2*x(1)*x(2) + x(2)^2; % Cost functionif nargout > 1 g(1) = 6*x(1)+2*x(2); g(2) = 2*x(1)+2*x(2);endoptions = optimset('GradObj','on');x0 = [1,1];[x,fval] = fminunc(@myfun,x0,options); |
使用矩阵运算代替迭代。
在matlab中矩阵运算都经过优化,速度较快。
matlab编程1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | if condition1, statement1elseif condition2, statement2else, statement3end |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | switch variable case constant1, statement1 case constant2, statement2, otherwise, statement3end |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | n = floor(real(double(n(1))));if mod(n,2) == 1 % Odd order M = oddOrderMagicSquare(n);elseif mod(n,4) == 0 % Doubly even order. % Doubly even order. J = fix(mod(1:n,4)/2); K = bsxfun(@eq,J',J); M = bsxfun(@plus,(1:n:(n*n))',0:n-1); M(K) = n*n+1 - M(K);else % Singly even order. p = n/2; %p is odd. M = oddOrderMagicSquare(p); M = [M M+2*p^2; M+3*p^2 M+p^2]; if n == 2 return end i = (1:p)'; k = (n-2)/4; j = [1:k (n-k+2):n]; M([i; i+p],j) = M([i+p; i],j); i = k+1; j = [1 i]; M([i; i+p],j) = M([i+p; i],j);end |
1 2 3 | for condition, statement;end |
1 2 3 | while condition, statement;end |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | a = 0; fa = -Inf;b = 3; fb = Inf;while b-a > eps*b x = (a+b)/2; fx = x^3-2*x-5; if fx == 0 break elseif sign(fx) == sign(fa) a = x; fa = fx; else b = x; fb = fx; endenddisp(x) |
1 2 3 4 5 | try statement1catch statement2end |
matlab作图
matlab提供了很多的方法来作图。通过图像我们能够直观的来观察数据中的重要特征。我们可以根据我们的数据来选择作图的类型,比如:line,bar,histogram,pie等;还可以用来做三维图形,比如:surfaces等。
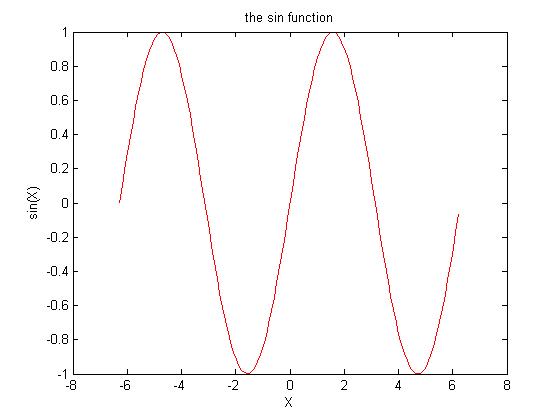
1 2 | >>X=-2*pi:.1:2*pi>>Y=sin(X) |
1 2 3 4 | >>plot(X,Y,'r');>>xlabel('X');>>ylabel('sin(X)');>>title('the sin function'); |
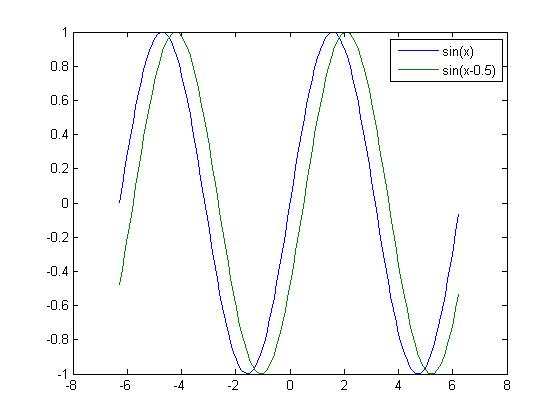
1 2 | >>plot(X,Y,X,sin(X-.5));>>legend('sin(x)','sin(x-0.5)'); %标注不同的函数 |
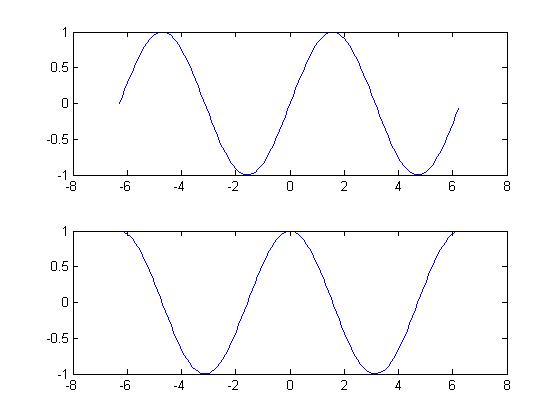
1 2 | >>subplot(2,1,1);plot(X,sin(X));>>subplot(2,1,2);plot(X,cos(X)); |
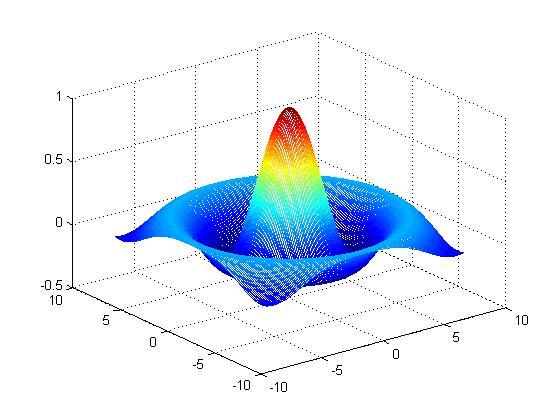
1 2 3 4 | >> [X,Y]=meshgrid(-8:.1:8);>> R=sqrt(X.^2+Y.^2)+eps;>> Z=sin(R)./R;>> mesh(X,Y,Z); |
1 | >>surf(X,Y,Z); |
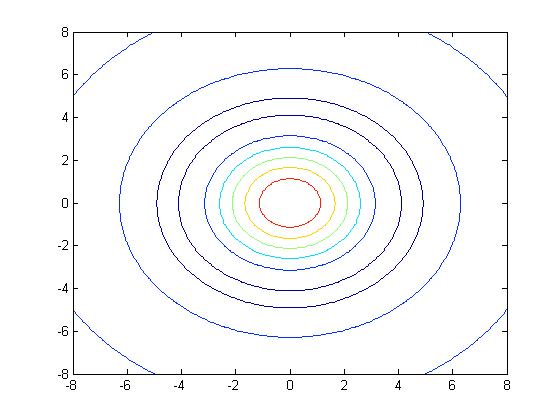
1 | >>contour(X,Y,Z); |
matlab入门
简介